Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
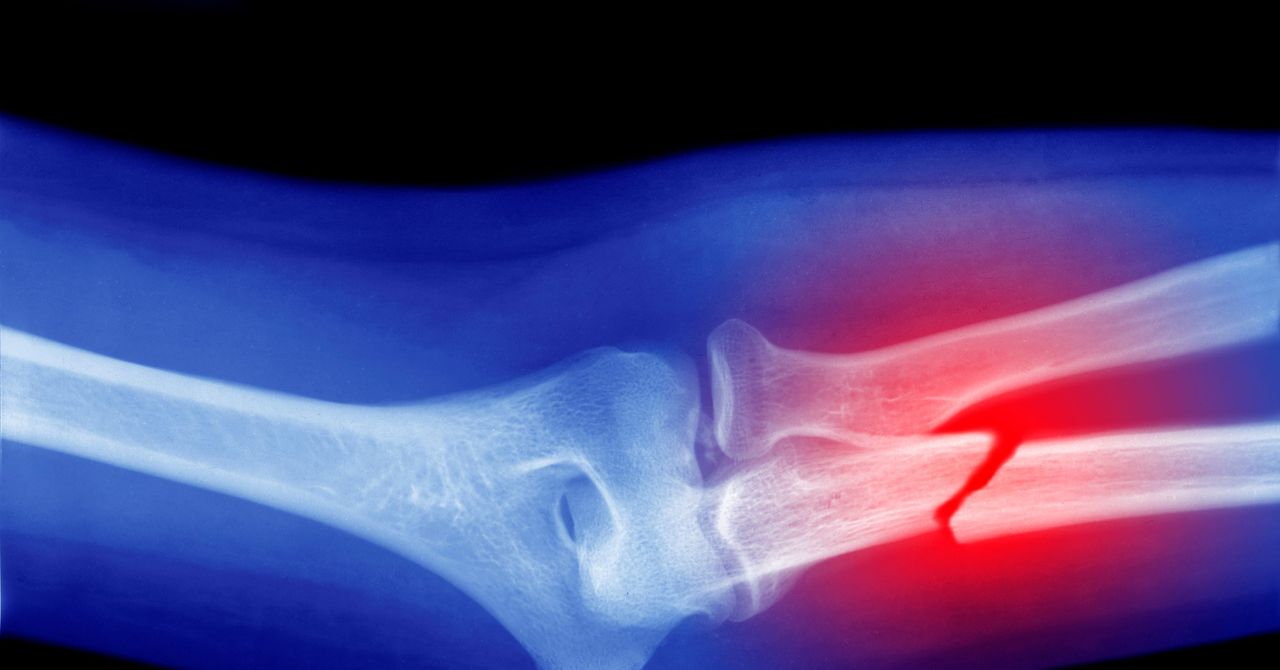
Microplastics could be A factor for dividing cases of osteoporosis worldwide, son Recently published research. The study shows that these tiny plastic particles, when they get into the body, disrupt the functionality of bone marrow stem cells that are essential for maintaining and repairing bone tissue.
Her bones are filled up throughout their life. Osteoporosis is an illness in which this process goes wrong, the bone exceeding the rate with which it is replaced. This leads to bones that weaken over time and break more often. The condition Has many risk factors– Age, gender, medication, nutrition, smoking and drinking and genetics influence them – with the disease that slowly develops over time. Often people do not recognize that they have the condition until they break a bone.
This new analysis, published internationally in the Journal Osteoporosis, is an potential new risk factor of microplastics. In research, 62 scientific articles were examined that had carried out various laboratory and ted tests on the possible effects of micro and nanoplasty on bones. The analysis of laboratory tests showed that microplastics stimulate the formation of osteoclasts, the cells generated by stem cells in the bone marrow that reduce the bone tissue to promote absorption, the process in which the body breaks off and eliminates old or damaged bones.
The study also showed that plastic particles in relation to bones reduce the livelihood of cells, induce premature cellular aging, modify gene expression and trigger inflammatory reactions. The combination of these effects creates an imbalance in which osteoclasts destroy more bone tissue than regenerated, which leads to an accelerated weakening of the bone structure.
When entering animal studies, the researchers found that the accumulation of microplastics in the body reduces the number of white blood cells – which indicates changes in bone marrow function. In addition, these animal studies indicate that the influence of microplastics on osteoclasts can be associated with a deterioration in the bone microstructure and the formation of irregular cell structures, which increases the risk of bone fragility, deformities and fractures.
“In this study, the observed disadvantageous effects culminated in the interruption of the skeletal growth of the animals,” said co -author Rodrigo Bueno de Oliveira in one Press release. “The potential effects of microplastics on bones are the subject of scientific studies and are not negligible.”
Oliveira, the coordinator of the laboratory for the evaluation of mineral and bone disorders in nephrology at State University of Campinas in Brazil, is now working with his team to further prove the relationship between the exposure between microplastic and bone deterioration. This research will initially evaluate the effects of microplastic particles on the femurures of rodents.
“Although osteometabolical diseases are relatively well understood, there is a gap in our knowledge of the influence of microplastics on the development of these diseases. Therefore, it is one of our goals to create evidence that indicate that microplastics could be a potential controllable environmental cause, for example, to explain the increase in the projected number of bone fractures,” said Oliveira.
Microplastics and nanoplasty are small plastic fragments – some so small that they are invisible to the mere eye that dismantle everyday objects when sunlight, wind, rain, sea water or abrasion. The main difference between the two is their size: microplastic dimensions of 1 micrometer (one thousandth of millimeters) to 5 millimeters, while nanoplasty is less than 1 micrometer. These particles have been proven around the world In natural environmentsas well as all overall human body And in meat, water and various agricultural products.
Studies have started to show that this type of plastic contamination can Health damage. Experts argue that this means that the world urgently has to reduce its use of plastics. Every year, more than 500 million tons of the material are produced worldwide, but only 9 percent are recycled, with a large part of the rest spreading into the environment and worsening.
This story originally appeared on WIRED in Spanish and was translated from Spanish.